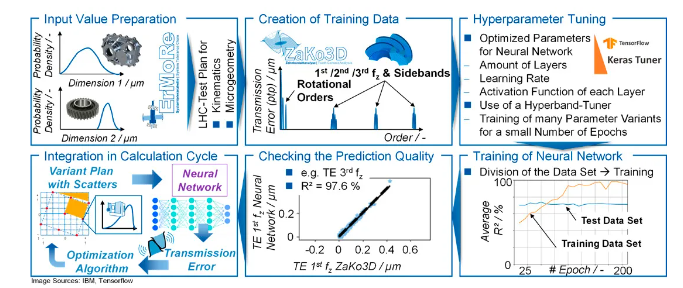
In order to use iterative metaheuristic optimization approaches, it must be possible to determine the excitation and cost parameters quickly in order to obtain a tolerance design with a reasonable amount of time. To increase speed, a meta model is therefore used which, after training with training data generated by a finite element-based tooth contact analysis, determines the total transmission error based on the gear micro geometry and axial position deviations. Figure 7 shows the procedure for creating and integrating such a meta model in the form of a deep neural network (DNN) with TensorFlow Keras based on Python (Ref. 39). After the creation of n = 6,330 training data sets in the FE-based tooth contact analysis, the training parameters are optimized, which takes about t = 2 h. This is done by varying the network parameters. The network is trained for a small number of epochs by varying the network parameters and a suitable parameter set is determined based on the training loss. This includes the number of layers, activation functions, number of neurons, etc. After training, the model is validated and the DNN is integrated into the cycle instead of the finite element-based tooth contact analysis. Figure 7 shows the training process and the prediction result for the transmission error (TE) in the third gear mesh frequency 3rd fz.
In detail, the optimized parameters were the hyperparameters listed in Figure 8 on the left. With a training effort of t ≈ 192 s, the predictions of the DNN compared to the calculation results from the finite element-based tooth contact analysis are shown for the first rotation order with regard to pinion and wheel as well as the first and second gear mesh order. For validation, n = 499 other variants not included in the training data set were used. The prediction qualities for all orders are R2 >88 percent and are therefore sufficiently suitable for prediction of the acoustic behavior. Better values were achieved for the rotational orders and their higher harmonics, see Figure 8, top. Isolated sidebands of the gear mesh orders proved to be more difficult to map due to their very low amplitudes and their partly stochastic dependence on modulation effects. The gear mesh frequencies (1st to 3rd fz) are not affected by this, as can be seen Figure 8, bottom. It is relevant for the training data that these are available within wide limits. This was ensured by limits that correspond at least to the factor f = 3 of the reference tolerances.
Next Evaluation and Weighting System for a Tolerance Design
BRIEF INTRODUCTION
Cnbearing is the No.1 bearing inquiry system and information service in China, dedicated to helping all bearing users and sellers throughout the world.
Cnbearing is supported by China National Bearing Industry Association, whose operation online is charged by China Bearing Unisun Tech. Co., Ltd.
China Bearing Unisun Tech. Co., Ltd owns all the rights. Since 2000, over 3,000 companies have been registered and enjoyed the company' s complete skillful service, which ranking many aspects in bearing industry at home and abroad with the most authority practical devices in China.




