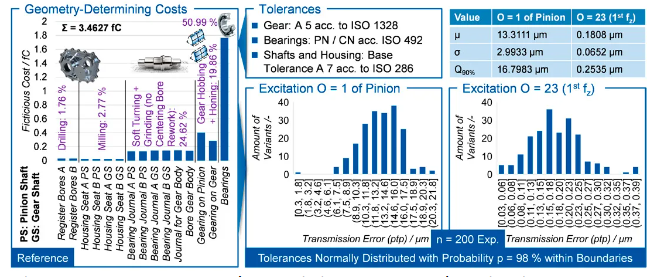
For comparison purposes, the possible variance in the excitation behavior is determined, which is set for a conventional tolerance design of the reference based on experience. For this purpose, the tolerance limits for profile and flank deviations are defined in accordance with quality class A 5 and normal or magnitude-normal distributions of the characteristic variables are assumed, see Figure 10, top center. Furthermore, quality class A 7 is used for the other basic tolerances on shafts and housings. The selected tolerance limits generally represent experience-based specifications that have not been further optimized. The cost calculation according to the procedure in the section “Modeling the Cost-Deviation Relationships for Geometric Features” results in geometry-relevant costs of C = 3.4627 fC. It should be noted that this is an optimized cost calculation according to the modelling, as it determines the most favorable process combination for this specific tolerance assumption. The costs are distributed over the roller bearings with p = 50.99 percent, which are included in the calculation with their full costs due to their consideration as purchased parts. In contrast, the other component costs only include the processes that determine the final geometry, meaning that the shares are lower. Especially, material costs, upstream process costs (e.g., casting of housing) are not included herein. It was determined that it is most economical to produce the dowel pin bores on the housing by drilling alone. The bearing seats can also be machined most economically in the reference design by pure milling. For the shaft shoulders, a combination of soft turning and grinding without reworking the centering bores is the most economical. For the gears, the method of hobbing with honing is proposed for both gears. It is noticeable that the production of the pinion gearing is stated to be more cost-intensive than that of the wheel, which initially seems implausible. This is due to the fact that different clampings are used during the gear-cutting process. While the pinion shaft is clamped on the bearing seats, which can have concentricity deviations of quality class A 7, the wheel is held in the bore. The possible concentricity deviations at the bearing seats result in clamping deviations (wobble), which cause a profile and helix angle deviation, which the honing process with the target specification A 5 has to eliminate. The effort required to achieve this target is far greater for the pinion shaft than for the wheel due to the clamping situation. As a result, the cost of the pinion also increases. Figure 10 below shows the distribution of the total transmission error for Min = 120 Nm. It can be seen that in particular the first gear mesh order O = 23 with respect to the pinion (corresponds to O = 87 with respect to the wheel) exceeds the nominal design of the excitation in Figure 9, top right by a factor f ≈ 2.5 with a 90 percent probability. This is only caused by the possible tolerance utilization.
Next FK Bearing Group Unveils Three 2026 Specialized Bearing Unit and Bearing Products
BRIEF INTRODUCTION
Cnbearing is the No.1 bearing inquiry system and information service in China, dedicated to helping all bearing users and sellers throughout the world.
Cnbearing is supported by China National Bearing Industry Association, whose operation online is charged by China Bearing Unisun Tech. Co., Ltd.
China Bearing Unisun Tech. Co., Ltd owns all the rights. Since 2000, over 3,000 companies have been registered and enjoyed the company' s complete skillful service, which ranking many aspects in bearing industry at home and abroad with the most authority practical devices in China.


