2025 China Agricultural Machinery Industry Sees Steady Progress and Quality Improvement
Abstract: In 2025, China's agricultural machinery industry will show a "steady and improving" development trend in a complex market environment. The industry's annual operating revenue is expected to reach 260 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of approximately 2%, achieving growth for two consecutive years. However, total profits will decrease by 2.39% year-on-year, highlighting the operational pressure on enterprises. The industry's operation exhibits six major characteristics: First, market vitality remains strong, with the Wuhan International Agricultural Machinery Exhibition reaching a record high; second, the industrial structure is optimized, with domestic mid-range brands dominating and foreign companies focusing on high-end niche markets, and digitalization and integrated solutions becoming trends; third, breakthroughs in core technologies, with progress made in the localization of key components such as hybrid chassis; fourth, the industrialization of new energy agricultural machinery is accelerating, with products such as hybrid tractors possessing global competitiveness; fifth, internationalization is increasing, with exports increasing by 32.3% year-on-year, becoming an important support for growth; sixth, competition is intensifying, with homogenization leading to the exit of some enterprises from the market.
Major product performance is differentiated: Tractor production decreased by 4.9%, but intelligent tractors and tracked models bucked the trend and increased; harvesting machinery as a whole declined, but the structure was optimized, with the proportion of large-feed models increasing. On the challenges side, supply-demand imbalances, rising costs, increased accounts receivable, and weak international market demand are constraining industry development. Looking ahead to 2026, the industry needs to promote high-quality development through technological innovation, product structure optimization, deepening its presence in international markets, and cost control, gradually stabilizing amidst adjustments.
In 2025, China's agricultural machinery industry will forge ahead in a complex and challenging market environment, showing a steady and positive development trend, optimized structure, and accelerated industrial upgrading.

The agricultural machinery industry in 2025 will have the following prominent characteristics.
First, despite several years of industry downturn, increased uncertainty due to natural disasters and other factors, and intensified market competition, the industry remains vibrant. This trend was well reflected at the Wuhan International Agricultural Machinery Exhibition, which boasted an exhibition area of 250,000 square meters, over 2,500 exhibitors, and 200,000 visitors—all record highs. Despite immense market pressure, businesses remain confident, and the industry demonstrates vitality.
Second, my country's agricultural machinery industry remains a sunrise industry, with agricultural production demanding and urgently requiring more sophisticated equipment. Through a transformation from "scale expansion" to "quality upgrading," the industry has formed a competitive landscape where domestic brands dominate the mid-range mainstream, while foreign brands focus on high-end niche markets. Products are becoming more diverse, moving from single products to comprehensive solutions. Companies are no longer limited to supplying a single agricultural machinery product but are offering integrated solutions covering the entire agricultural production process, with digital and intelligent technologies becoming increasingly prominent. This continuous enrichment of product types has led to widespread development in various sub-sectors. In addition to traditional agricultural machinery, the commercialization of equipment related to horticulture and vegetable processing, among other cash crops, is accelerating. The application scenarios for agricultural drones are constantly expanding. Beyond traditional pesticide spraying, their use in areas such as agricultural product handling, aerial seeding, aerial fertilization, and aerial pollination is becoming increasingly widespread, making it a rapidly growing sub-sector.
Third, the resilience of China's agricultural machinery development is evident. Nearly 70% of the exhibitors at the Wuhan exhibition were component manufacturers, with leading component companies attracting significant attention. Their exhibits of new hybrid powertrain chassis, power-shift chassis, and continuously variable transmission chassis signify a solid step forward in the self-sufficiency of core technologies and key components in China's agricultural machinery industry, and a significant improvement in the quality and reliability of the agricultural machinery supply chain.
Fourth, the industrialization of new energy agricultural machinery is accelerating. By 2025, the industrialization of high-efficiency, low-consumption agricultural machinery such as hybrid tractors, hybrid wheat harvesters, hybrid cotton harvesters, and electric high-speed seeders will advance rapidly, marking a leap forward for China's agricultural machinery industry. my country's new energy agricultural machinery demonstrates global competitive advantages and strong industrial development potential, gaining recognition and affirmation from the government and the market.
Fifth, the internationalization of China's agricultural machinery industry is continuously improving. Foreign agricultural machinery companies are showing strong momentum and sustainability in China, providing increasingly synchronized technologies and products with global standards. Their high-end, state-of-the-art agricultural machinery has a market and proven track record in China. The Wuhan Agricultural Machinery Exhibition is attracting more and more foreign buyers, becoming a new channel for us to expand overseas.
Sixth, under the pressure of industry downturn, competition among enterprises is becoming more intense. Product homogenization continues to intensify, the concentration of major agricultural machinery products in the industry is increasing, and enterprises lacking technological innovation are finding it difficult to survive. Some brands have become relics of the past, and some enterprises have either ceased production or withdrawn from the competition.
Working together to achieve growth
According to the National Bureau of Statistics, from January to November, 2,327 large-scale agricultural machinery enterprises nationwide achieved operating revenue of 237 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of approximately 1.68%. The industry's total operating revenue for the year is projected to reach 260 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of around 2%. Although the growth rate is relatively small, this marks the second consecutive month of growth since the industry experienced a significant decline (-9.62%) in 2023, reaching a historical low, which is truly remarkable. Faced with various market risks, challenges, and uncertainties, supportive policies and the hard work of enterprises have led to new breakthroughs in industrial restructuring and market adaptability.
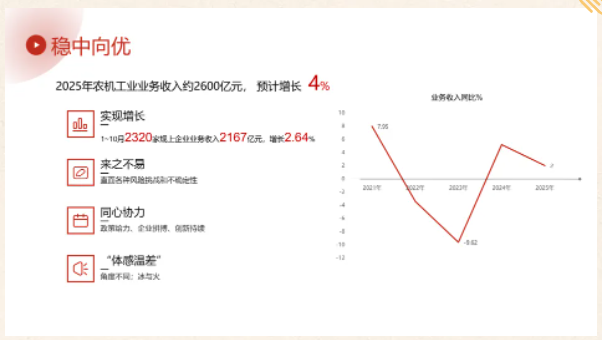
In 2025, while the industry's operating revenue showed positive growth, many enterprises (especially small businesses) felt a deep chill in the market. This difference stemmed from several factors: First, the difference in statistical methods. Data in the national statistical system came from large-scale agricultural machinery enterprises. These large-scale enterprises have brand influence, sufficient operating funds, and a stronger ability to cope with market downturns. Meanwhile, some small enterprises, facing market pressure, were trapped in a cycle of homogeneous, low-price competition, experiencing operational difficulties and a significant decline in revenue. Second, agricultural machinery products and services cover a wide range of areas and are diverse. Product sales saw both growth and decline. 75% of sub-sectors, such as parts and fishery machinery, saw year-on-year growth. However, products like tractors declined, and since tractor revenue accounted for 19.7% of the entire industry, its poor performance had a significant impact on the sector. Third, there were significant differences in regional markets. The degree of impact of natural disasters on agricultural production across the country, and the intensity of adjustments to the key tasks of machinery purchase subsidies, all had varying effects on the agricultural machinery market. Fourth, domestic sales and exports showed contrasting trends. According to China Customs statistics, agricultural machinery exports increased by 32.3% year-on-year in 2025, making a significant contribution to stabilizing industry growth.
From January to November 2025, the total profit of the agricultural machinery industry decreased by 2.39% compared to the same period last year, failing to achieve synchronous growth. The industry's average gross profit margin was 17.8%. The proportion of loss-making agricultural machinery enterprises above a certain scale reached 24%, with tractor enterprises accounting for as high as 33%. Listed companies, representing the industry's advanced level and serving as a market barometer, saw a general decline in revenue and profits for both domestic and international listed agricultural machinery companies in 2025. This was mainly due to insufficient market demand leading to low capacity utilization, coupled with high inventory levels and increased capital costs. To promote sales, companies increased the use of credit sales and interest subsidies, resulting in a 10.9% year-on-year increase in accounts receivable and a 57.35% increase in financial expenses, further squeezing profit margins.
The industry in 2025 exhibited a clear characteristic of "high start, low finish, and failure to meet expectations." In the first quarter, influenced by the increased market activity in the fourth quarter of the previous year and the incentives from the national agricultural policies at the beginning of the year, enterprises generally had confidence in the market. Many leading enterprises set annual growth targets of around 20%, and the industry entered a production boom, with business revenue growing by as much as 9.42% in March. In the second quarter, affected by severe drought and other factors, the market took a sharp turn for the worse and fell into a "frozen period." It was supposed to be the peak sales season, but there were very few buyers in some large agricultural machinery markets, and manufacturers had no choice but to follow suit and implement production restrictions or shutdowns. The third quarter was supposed to be the peak season for the production and sales of products such as corn harvesters, but it was hit by a very severe autumn flood, resulting in weak growth. In the fourth quarter, enterprises shifted their focus to digesting inventory, and there was no seasonal rebound as in previous years, with the market remaining at a low level.
Major product prices fluctuated, but technological innovation yielded positive results.
In 2025, the National Bureau of Statistics reported that 117 tractor manufacturers produced a total of 465,200 tractors, a 4.9% decrease year-on-year. Large tractors remained the same as the previous year, while medium and small tractors saw a significant decline. Leading tractor manufacturers produced 275,200 large and medium-sized tractors, a decrease of 8.46% compared to the previous year. In a sluggish market, cost-effective power-reversing intelligent tractors stood out with significant growth; tracked tractors, supported by national policies, became a new growth point; the expansion of demand for cash crop production led to a decrease in demand for traditional tractors and an increase in demand for special-purpose tractors. In terms of power distribution, the pattern of "large tractors dominating, medium tractors reigning supreme" remained unchanged. Medium-sized tractors with 50-60 horsepower and 70-80 horsepower still had the largest market share, while tractors with more than 300 horsepower only produced around a thousand units annually. In the face of homogeneous competition, focusing on the mainstream market remained crucial for the survival of enterprises; 33% of leading tractor manufacturers achieved performance growth by focusing on the large and medium-sized tractor market. In 2025, the illegal production of poorly made tractors that failed to meet the National II emission standards impacted the market. In the second half of the year, this chaotic situation was addressed by four national ministries, and the market environment gradually improved. However, competition in the tractor industry remains fierce; companies lacking technological advantages are struggling to survive. New companies like Lingong have entered the market, while a number of established companies have exited.
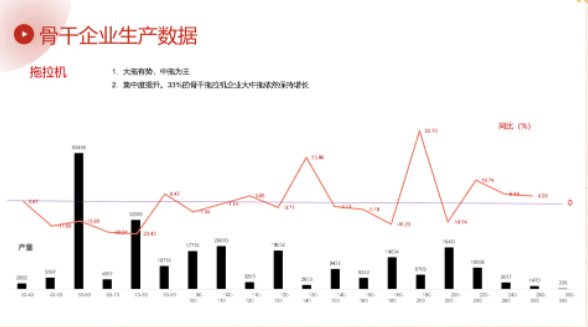
The harvesting machinery market exhibited an overall decline but structural optimization trend, with significant differences in performance across different product categories. Leading enterprises produced 18,600 self-propelled wheeled grain harvesters throughout the year, a 31.01% year-on-year decrease, with sales down 35.44%. The year-on-year decline in production was attributed to several factors, including increased feed capacity, improved reliability, and significant improvements in harvester efficiency brought about by intelligent upgrades. Decreased operator earnings and market saturation in major grain-growing areas were also major contributing factors. Product structure continued to optimize, with longitudinal axial flow high-feed models becoming the mainstream products. Products with a feed capacity of 10-11 kg accounted for 60% of the market, and 12-13 kg products accounted for 32%. Lovol maintained its leading position with a 55% market share. After several years of technological accumulation, China YTO's wheeled harvesters began to return to the market, while Hebei Yinghu's wheeled harvesters began to emerge.
Leading enterprises produced 23,800 self-propelled corn harvesters, a 12.30% year-on-year decrease. Affected by factors such as years of fluctuating corn prices and the autumn floods of 2025, the market share of three-row and four-row wheeled harvesters (42.78%) declined, while two-row, six-row, and seven-row wheeled harvesters saw significant growth, indicating a diversification of regional production patterns and demands. To cope with the autumn floods, four-row tracked corn harvesters surged by 52.17%, while two-row and three-row tracked corn harvesters declined. Grain harvesters saw a significant decrease, influenced by multiple factors. Harvesting across the entire corn value chain was favored, while harvesters that harvest both stalks and ears continued to grow.
Leading enterprises produced 75,200 full-feed tracked rice harvesters, a year-on-year increase of 8.84%. Driven by the national "trade-in" program, subsidies for old machines from major enterprises, and strong demand for tracked harvesters in dryland areas and for minor grains, the tracked harvester market saw a high replacement frequency, with a clear trend towards larger feed capacities, particularly with a rapid increase in the proportion of 7kg and 10kg models. Domestic companies primarily target the 10kg market, while foreign companies like Kubota and Yanmar focus on the 7kg market. Japanese companies still hold a 14% market share in full-feed tracked rice harvesters, with Kubota and Yanmar projecting strong growth by 2025. Companies in Chongqing and other regions have made technological progress in producing rice harvesters for hilly and mountainous areas, leading to a continuous increase in mechanized rice harvesting rates in these regions. A comprehensive analysis, excluding the significant increase in exports, shows that the domestic tracked harvester market actually declined, with the purchase subsidy system indicating a year-on-year decrease of approximately 11%.
Leading enterprises produced 55,500 rice transplanters, a year-on-year decrease of 13.50%. High-speed riding-type rice transplanters, due to their high operating efficiency and intelligent features, held a 59.25% market share, but production decreased by 24.54% due to spring drought, diversified planting methods, and adjustments to subsidy policies. Hand-held rice transplanters, with their advantages of low price and short payback period, saw production buck the trend, increasing by 9.88% driven by agricultural machinery scrapping and replacement subsidies in Northeast China. Industry concentration has increased, with over 50 manufacturers of high-speed riding rice transplanters, the top five accounting for 85% of the market. Japanese companies, leveraging advanced technology and high quality, have a significant market influence, while domestic high-speed rice transplanters from companies like Jiangsu Jiufu, with their cost-effectiveness and service advantages, have gradually expanded their market share to over 50%.
The baler market continued its downward trend, with output decreasing by 16.41%. Affected by the sluggish livestock industry and the impact of second-hand equipment imports, previously fast-growing products such as large-scale forage balers and straw wrapping balers have also experienced significant declines.
Exports have become an important force supporting industry growth.
In 2025, against the backdrop of rising global trade protectionism and escalating geopolitical conflicts, China's agricultural machinery exports achieved a significant increase against the trend, becoming a key force supporting the industry's development. From January to November, the export delivery value of agricultural machinery enterprises above a certain scale reached 47.9 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 13%; the annual export volume of large and medium-sized tractors from leading enterprises increased by 22.15%, higher than the overall industry growth rate.
Exported products remained mainly low-to-mid-range, but their competitiveness continued to improve. Tractors below 150 horsepower accounted for 93.8% of total exports, with 50-horsepower and 80-horsepower tractors being the main export models, reflecting the dominant position of Chinese agricultural machinery in the international mid-range market. Meanwhile, breakthroughs were achieved in high-end product exports, with combine harvester exports increasing by over 55%, accounting for 20% of total production. Among them, the export of tracked harvesters from leading enterprises increased by 54.49%, mainly exported to Southeast Asian countries such as India and Indonesia. The significant increase in harvester exports has changed the international market's perception of the quality of Chinese agricultural machinery products.
Export markets diversified, with significant growth in key regions. Tractor exports to European markets such as the UK, France, and Germany grew by about 50%; exports to conflict-affected regions like Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus saw cautious growth, with nearly 30% increase; while exports to the US market declined for some products, the decrease was less than expected. Cotton harvester exports performed exceptionally well, reaching 1,594 units, with over 1,300 units exported to Uzbekistan alone. This also boosted cotton gin exports, achieving complete export of production models, product technology, standards, and operational solutions, marking a shift in China's agricultural machinery exports from single-product exports to full-chain service exports.
Exports saw comprehensive growth across all categories, with component exports playing a prominent role. In addition to complete machines such as tractors, combine harvesters, and rice transplanters, exports of components such as plows, clutches, and couplings also increased. Component exports have maintained growth for over a decade, becoming a crucial force supporting industry growth.
Pressures compounded and risks remain; the industry faces multiple challenges.
From an internal perspective, the main challenges are the imbalance between supply and demand and the increasing pressure on business operations.
First, the contradiction between supply and demand is prominent. The coexistence of overcapacity in low- and mid-range products and insufficient supply in high-end products has not been fundamentally resolved. Severe homogenization of some products has led to frequent price wars, squeezing profit margins for enterprises. Meanwhile, the supply of agricultural machinery in hilly and mountainous areas, intelligent equipment, and specialized machinery for cash crops remains insufficient, failing to meet the diversified market demand.
Second, business operations are under increasing pressure. The persistently high cost of production materials has led to increased production costs for enterprises; accounts receivable increased by 12.45% throughout the year, making cash recovery difficult and increasing business risks.
Third, market demand is insufficient. Low agricultural production efficiency is a significant factor restricting demand for agricultural machinery. The sharp decline in grain prices echoes the slow growth of the agricultural machinery industry, a trend observed in international markets such as Europe and the United States. Furthermore, farmers' incomes have decreased due to natural disasters such as autumn floods, weakening their willingness to purchase machinery; the trade-in policy has not met expectations, resulting in insufficient release of new demand and low market activity.
From an external perspective, the downturn and uncertainty in the international agricultural machinery market have further intensified. On the one hand, the global agricultural machinery industry is in a downturn. Major agricultural machinery markets such as the United States, Europe, Japan, and India are all experiencing declines. US tractor production fell by 9.7% year-on-year, and harvester production fell by 38.3%. The EU economy has continued to decline, and agricultural and agricultural product prices have been impacted by trade agreements. The Japanese agricultural market is affected by the US's open agricultural import policy, resulting in weak demand. The sluggish global agricultural machinery market puts pressure on the continued growth of China's agricultural machinery exports.
On the other hand, international uncertainty is increasing. Rising trade protectionism, changes in tariff policies, and supply chain fragmentation are affecting agricultural machinery exports. Escalating geopolitical conflicts are increasing export risks to some overseas markets. Enterprises are concerned about the export situation in 2026, and the "rush to export" effect may diminish, putting the sustainability of high-speed export growth to the test.
Furthermore, some high-end markets still rely on foreign brands, and the supply capacity of domestically produced high-end equipment needs to be improved, exacerbating the industry's "involution" phenomenon. Some companies continue production even at a loss in order to dilute fixed asset depreciation, stabilize cash flow, and maintain market share, leading to further price reductions and creating a vicious cycle of "prisoner's dilemma" competition. This not only squeezes their own profit margins but also disrupts market order and is detrimental to the long-term healthy development of the industry.
Rising against the tide and standing at the forefront, innovation continues to drive progress.
Despite numerous challenges facing the industry, the underlying trend of high-quality development is becoming increasingly prominent, with innovation becoming the core driving force for its progress. National major infrastructure projects have provided financial support to the agricultural machinery industry, further enhancing the competitiveness of leading enterprises and state-owned enterprises. Intelligent production equipment is widely used in the industry, with many component manufacturers and small agricultural machinery manufacturers introducing automated warehouses, intelligent logistics, and other systems to achieve intelligent management of the entire production, procurement, and logistics process.

Investment confidence remained stable. Despite downward pressure on the national economy, investment in the agricultural machinery industry bucked the trend, with the industry's overall asset growth rate reaching 6%. Private enterprises were particularly prominent in their investment. Chongqing Weima built a factory in Thailand and invested heavily in modern testing equipment. Companies like Weifang Guhe and Jianhu Jinganzi continued to increase their equipment investment, reflecting their confidence in the industry's long-term development.
Scientific and technological innovation yielded fruitful results. Hybrid agricultural machinery became a hot topic in the industry, and green energy equipment technologies such as electric seeders matured. Breakthroughs were achieved in the localization of key components, meaning that China is "making fewer and fewer agricultural machines it cannot manufacture, and the agricultural machines it can manufacture are getting better and better."

In 2026, we must remain confident, patient, and move steadily towards a brighter future.
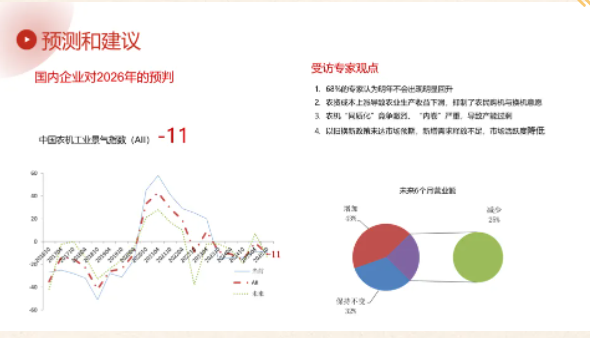
Considering both domestic and international environments, the agricultural machinery industry generally holds a cautious attitude towards its performance in 2026. A survey by the China Agricultural Machinery Industry Association shows that 68% of experts believe the industry will not see a significant rebound in 2026. International counterparts also hold cautious expectations, believing that future prospects will not change significantly and global demand will remain stable.
However, there are also some positive factors. The 2025 Central Economic Work Conference clearly stated that a more relaxed fiscal policy will be implemented to stabilize enterprises and the market, bringing policy benefits to the agricultural machinery industry. Under national macro-control, reduced grain imports are expected to drive a gradual recovery in domestic grain prices, improving agricultural production efficiency. New products such as hybrid and electric agricultural machinery, as well as niche markets such as hilly and mountainous agricultural machinery and intelligent equipment, still have significant growth potential. Technological upgrades and innovative applications within the industry will lay the foundation for recovery.

Overall, the agricultural machinery industry will face continued pressure in 2026, but a significant decline is not expected; it will gradually stabilize through adjustments.
Faced with a complex market environment, the agricultural machinery industry needs to adhere to high-quality development as its core principle, focusing on structural optimization, technological innovation, and efficiency improvement to promote the industry's continued healthy development.
First, optimize product structure and focus on core markets. Enterprises should avoid blind expansion and homogeneous competition, increasing investment in high-end areas such as agricultural machinery for hilly and mountainous areas, intelligent equipment, and new energy agricultural machinery. They should prioritize key agricultural machinery equipment related to food security, as well as niche markets such as cash crops and livestock farming, cultivating new growth points.
Second, strengthen technological innovation and enhance core competitiveness. Focus on tackling key technologies for core components such as power shifters and CVT transmissions, promoting the industrial application of new technologies such as hybrid and electric agricultural machinery, and increasing the localization rate of core components.
Third, cultivate the international market and expand growth space. Optimize overseas layout by establishing factories overseas, exporting technology, and localizing production to circumvent trade barriers; enhance product adaptability to international markets to meet the technical standards and usage needs of different countries and regions; improve overseas service networks, enhance after-sales service levels, and strengthen international market competitiveness.
Fourth, reduce operating costs and mitigate financial risks. Optimize production processes and improve capacity utilization; strengthen accounts receivable management and establish a sound risk control mechanism; rationally control inventory to alleviate cash flow pressure; SMEs can focus on niche markets and pursue a specialized, refined, and innovative development path to enhance market competitiveness and risk resistance.
Overall, in 2025, China's agricultural machinery industry achieved steady growth despite pressure and made significant progress in transformation, laying the foundation for the industry's long-term healthy development. Although 2026 faces many challenges, with the in-depth promotion of high-quality development, the continuous efforts of innovation-driven development, and the continuous optimization of the policy environment, the agricultural machinery industry is expected to overcome the adjustment period and achieve more stable and higher-quality development. Enterprises need to maintain confidence and patience, and move steadily towards long-term goals. They should focus on building core capabilities, seize opportunities in industry transformation, and achieve long-term sustainable development.
1.The news above mentioned with detailed source are from internet.We are trying our best to assure they are accurate ,timely and safe so as to let bearing users and sellers read more related info.However, it doesn't mean we agree with any point of view referred in above contents and we are not responsible for the authenticity. If you want to publish the news,please note the source and you will be legally responsible for the news published.
2.All news edited and translated by us are specially noted the source"CBCC".
3.For investors,please be cautious for all news.We don't bear any damage brought by late and inaccurate news.
4.If the news we published involves copyright of yours,just let us know.
Next Deepening School-Enterprise Collaboration to Empower Student Employment--China Nan an Industrial School Visits FK Bearing Group for Special Internship and Employment Research
BRIEF INTRODUCTION
Cnbearing is the No.1 bearing inquiry system and information service in China, dedicated to helping all bearing users and sellers throughout the world.
Cnbearing is supported by China National Bearing Industry Association, whose operation online is charged by China Bearing Unisun Tech. Co., Ltd.
China Bearing Unisun Tech. Co., Ltd owns all the rights. Since 2000, over 3,000 companies have been registered and enjoyed the company' s complete skillful service, which ranking many aspects in bearing industry at home and abroad with the most authority practical devices in China.




